
How To Format A Write Protected USB Pendrive
You’re trying to save some data on your USB flash drive, but there happens to be a problem. Any attempt to save them displays the message that the drive is currently “write protected”. How can this be?
The drive would not even allow you to reformat it, and there is no visible way to enable or disable write protection. Puzzled? Here’s how to format your write-protected USB Pendrive and start making use of it again.
How to Remove USB Write Protection With Diskpart
Before starting, insert your Pendrive into your computer’s USB drive port.
Windows has a built-in disk partition management tool known as Diskpart. You can open this by clicking the Windows key + R, entering cmd, then click on Enter.
User Access Control will ask you to confirm the action. Click on Yes to continue.
You should now see the CMD, which is a command-line tool. At the prompt, enter
diskpartA new CMD window will open up, with a new DISKPART prompt. It is now time to see the disks that are attached to your computer:
list diskThe resulting table will show the available devices. But which is your USB drive?
Disk 0 would be your computer’s system drive. This is the drive that your Windows installation is on. If you have several partitions, these will be numbered sequentially. Take note of the size that is displayed for each disk.
With a USB flash device connected, (which will be Disk 1 or higher) you should be able to locate it by its comparatively low capacity.
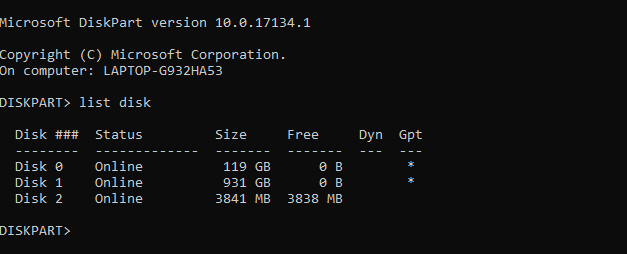
Image Credits: Makeuseof
In the image above, while the Disk 0 is 119GB and Disk 1 is 931GB (two partitions on the same drive), Disk 2 is 16GB.
Therefore, Disk 2 is the USB flash drive that was inserted. You should be able to check the capacity on the device itself, as this is usually printed on a casing of the drive. If not, you would be able to confirm it in Windows Explorer.
Select the Right Disk!
Before proceeding, be very sure that you have located the USB drive. Making the effort to be entirely certain at this stage is essential to the integrity of the data on your computer!
Once you’re certain, it is now time to select the disk. In our example, that means entering
select disk 2This will now be confirmed with the message that your disk 2 is now the selected disk. Next, request for your disk attributes:
attributes diskSeveral pieces of information will be presented. Check the first line. This is the Current Read-only State. If you are not able to write to the disk or reformat it, then Current Read-only State will be set to Yes.
You can easily remove the write protection on your Pendrive with the command below.
attributes disk clear readonlyIf successful the following message would be displayed “Disk attributes cleared successfully.”
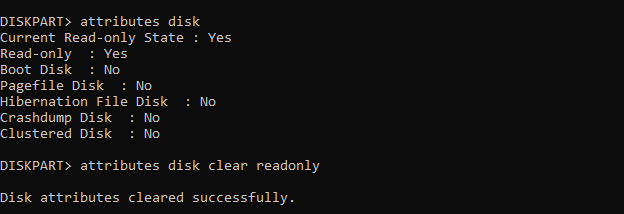
Image Credits: Makeuseof
Are you happy with losing the data on your USB flash drive? if yes, You can format the drive by using the diskpart’s clean command. First, make sure that the disk is selected:
select disk 2 cleanYou can then create and format a partition:
create partition primary format fs=ntfsWait for this to complete—you should now have a completely working and well-formatted USB flash drive!
Check the write-only status of the drive-by copying a small file to it.
Didn’t Work? USB Formatting Utilities to Try
Below is a free tool that you can use to format your USB drive in the case of a write protect error. You can use this as an addition to, or instead of using a Diskpart. It is very useful if you don’t like getting your hands dirty by using the command line!
SD Formatter
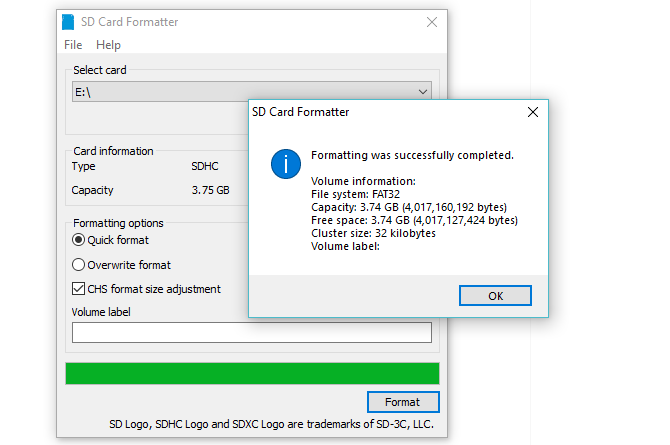
Image Credits: Makeuseof
Although SD Formatter is clearly designated for formatting SD cards, the tool is also compatible with USB flash drives. After all, A USB flash drive is just an SD card that is attached to a USB interface.
Simply attach the device to your PC, select the drive and a formatting option, and hit Format.
Download: SDFormatter (Free)
Your write-protected USB Pendrive, Formatted
By now you should have removed the write protection on your USB flash drive and would have reformatted it. This may have been done by using Diskpart on Windows, or by using the third-party utility app above.

